Translation Tools
 The translation process is both technical and creative. The translator needs a good tool to concentrate on producing a high-quality translation that meets the client’s satisfaction. Translation tools, software, and systems are made to take care of all technical aspects that save translators time and reduce effort to focus on the translation activity.
The translation process is both technical and creative. The translator needs a good tool to concentrate on producing a high-quality translation that meets the client’s satisfaction. Translation tools, software, and systems are made to take care of all technical aspects that save translators time and reduce effort to focus on the translation activity.
Translation tools have been affected by modern technology development. A few years ago, translators used to edit software to write their translation. Nowadays, there are lots of translation tools.
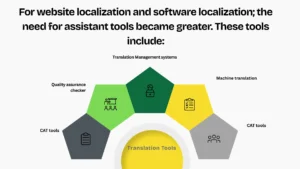
For website localization and software localization; the need for assistant tools became greater. These tools include:
- CAT tools
- Quality assurance checker
- Translation Management systems
- Machine translation
CAT Tools
Nowadays, most professional translators use Computer Aided Translation (CAT) tools. CAT refers to software used by human translators during the translation process to improve productivity, save time, and raise efficiency.
Examples of commonly used CAT tools:
- SDL Trados Studio
- SDL Passolo
- Kilgray memoQ
- Memsource
- XTM
- Alchemy Catalyst
CAT tools cover a wide range of features, including:
- Spell/Grammar checker, Autocorrect
- In-context review
- Text search
- Terminology software
- Translation Memory
- Concordance
- Alignment
- Quality Assurance
CAT tools can be available both offline and online. Online CAT tools work in browsers and desktop apps, supporting formats such as MS Office, InDesign, and AutoCAD.
Management Tools
For businesses looking to go global, Translation Management Systems (TMS) handle complex tasks and make collaboration between LSPs and clients easier. TMS manages workflow, translation memory, terminology, machine translation, and reporting.
Main purposes of TMS:
- Automated workflow management
- Centralized Translation Memory
- Terminology management
- Integration with Content Management Systems (CMS)
The integration of CMS with TMS automates content updates, reduces costs, and raises efficiency, ensuring multilingual audiences stay up to date.
Machine Translation
Machine Translation (MT) is a sub-field of computational linguistics that uses software to translate between languages. It helps increase productivity and speed up translation tasks.
Approaches of MT:
- Rule-based: Uses grammar rules and dictionaries.
- Statistical system: Learns translation patterns from large data sets.
- Neural Machine Translation: Teaches software to produce more natural translations; popular in recent years.
Types of MT:
- Generic MT (e.g., Google Translate, Bing)
- Customizable MT (trained for specific domains such as medical, legal, or IT)
MT often requires human editing (post-editing) to achieve high-quality results. Post-editing is the future trend of localization.
Future of Translation Tools
Despite advancements in CMS, TMS, and MT, further development is needed to consistently meet high-quality standards. The future of translation tools will likely focus on higher accuracy, efficiency, and seamless integration with business processes.
In your opinion, what development can we see in the translation tools in the future?