Video game age ratings
There are lots of different video game ratings and different countries have different definitions of inappropriate content and that is exactly why game developers release different modified versions of their games. This blog will be discussing the age rating system for video games in Saudi Arabia followed by a comparison between the biggest rating organizations around the world and some reasons why video games are being banned in certain countries or being culturally adapted to fulfill set restrictions.
Saudi Arabian Age Rating System for Video Games
The age rating system was implemented in Saudi Arabia during August 2016 by the General Commission for Audiovisual Media (GCAM). GCAM is an agency within the Government of Saudi Arabia, established in 2012. It is responsible for the development, regulation, and supervision of audiovisual media transmission in the Kingdom and reports to the Ministry of Media but is independent of it.
The first video game to be rated under the GCAM is the PlayStation 4 exclusive Uncharted 4: A Thief’s End. The current age rating system in Saudi Arabia is divided into five categories:
- 3: Suitable for those aged 3 +
- 7: Suitable for those aged 7 +
- 12: Suitable for those aged 12 +
- 16: Suitable for those aged 16 +
- 18: Suitable for those aged 18 +
Comparison Between Different Video game age ratings Systems in Different Countries
The different age rating organizations around the world correspond with a description which could be in the form of numbers or letters to indicate the minimum recommended age to play the game. Either way the purpose of the classification is to inform the buyer whether it is the parents or the children themselves that there might be undesirable content.
Below are some of the biggest rating organizations around the world:
| Country | Organization | Age Rating System |
| United Arab Emirates | National Media Council (NMC) | NMC Rating System |
| Europe & United Kingdom | Pan European Game Information (PEGI) | PEGI |
| Germany | Unterhaltungssoftware Selbstkontrolle (USK) | USK |
| United States of America | Entertainment Software Rating Board (ESRB) | ESRB |
| Canada | Entertainment Software Rating Board (ESRB) | ESRB |
| Japan | Computer Entertainment Rating Organization (CERO) | CERO |
| South Korea | Game Rating and Administration Committee (GRAC) | GRAC Rating System |
| International | International Age Rating Coalition (IARC) | IARC (Adapts to regional standards) |
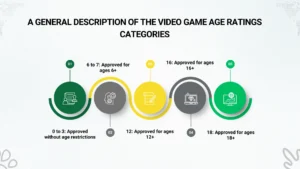
A General Description of the Video game age ratings Categories
In terms of minimum age recommendation, Video game age ratings systems are roughly similar across different countries. For example, the PEGI rating 3 indicated being suitable for everyone which is roughly similar to USK rating 0 or the ESRB which use letter descriptions instead of numbers to refer to being suitable for everyone with E-Everyone.
0 to 3: Approved without age restrictions
This category is completely family friendly with no signs of violence or any sort of offensiveness.
6 to 7: Approved for ages 6+
This category includes a higher sense of competition than the one above and could have horror moments, rare cursing and signs of fantasy violence.
12: Approved for ages 12+
This category becomes more offensive language and more realistic violence but is still relatively fictitious.
16: Approved for ages 16+
This category comes in a realistic, frequently including violence, horror, military missions and overuse of offensive language.
18: Approved for ages 18+
This category contains explicit: animated blood visuals, heavy cursing content and injecting ideologies, heavy violence in terms of killing/self-cutting/ fighting/suicide, horror and threatening environment, illegal drug intake and selling, mature content and discrimination against religious or ethnic groups.
Why Are Some of the Famous Video Games Being Banned in Some Countries?

It does not necessarily have to be due to promoting the content included in the 18+ category or even touching upon controversial topics. The following are some examples:
- EA Sports MMA- Denmark: The game was not banned due to the excruciating violence, it was the energy drinks. The game featured in-game advertisements for energy drinks and advertising for such products is illegal in Denmark. Producing a version without these advertisements was suggested by Denmark, but the game producers decided to stop selling it in Denmark instead.
- Grand Theft Auto- Thailand: This game lead to real-life consequences. Back in 2008, a man stabbed his taxi driver to death and when the police officers caught him, he said that killing seemed easy in Grand Theft Auto and he needed the taxi money to reserve a spot in an internet cafe and play the game.
- The Pokemon Trading Card Game- Saudi Arabia: It was banned during 2001 because the symbol used to represent energy resembled “the star of David” which is well known to be connected to international Zionism and this was not tolerated in Saudi Arabia by any means.
- Postal 2- New Zealand: New Zealand’s ban on the game cites “Gross, abhorrent content: Urination, High Impact Violence, Animal Cruelty, Homophobia, Racial, and Ethnic Stereotypes”. The ban is taken very seriously to the extent that the penalty of being caught owning a copy is $1,400.
- Call of Duty: Black Ops 2- Pakistan: The game was banned by the Pakistani authorities because they saw their country being portrayed in a negative light.
For other countries it was not only about banning certain video games, instead completely freezing publishing new video games until new rules are set in order to protect the young generation from an industry considered harmful in some countries around the world.
For instance, China’ s Government freezing video game licensing for 9 months during 2018 and resuming with strings attached and those include:
- Not having dead bodies or blood pools in any color or form. Games including dead bodies or skeletons are being turned into gravestones in the Chinese version and blood portrayed as a green or blue slimy substance are still not allowed.
- Implementing self-censorship and anti-addiction systems which turned off in-game rewards after the underage players have played a certain number of hours per day.
Banning mahjong where players could gamble with real money in the game, looking at the fact that gambling is illegal in China.
Did You Know Saudisoft Offers Cultural Adaptation Reports?
With the era of globalization, game developers who want to release their games into global markets go through the process of cultural adaptation in order to localize their content to suit the market they want to launch in. The report could focus on several aspects such as: usage of colors, number formats, character design, myths and legends, songs, and sociocultural, economic and political issues.
Age rating system in Saudi Arabia.