How Artificial Intelligence is changing the language industry
Your Localization Roadmap
AI might have sounded like science fiction a few years ago, but it has actually been part of our world for quite a while. It dates back to 1956 when the Logic Theorist was created by John McCarthy to mimic the problem solving skills of a human.
With the advancements that have been taking place between 1956 and 2021, AI technology now works with something more complex than the machine learning technology called deep learning, which imitates the brain functionality and analyzes the situations based on the overlapping data it’s provided with. With AI algorithms becoming more sophisticated on a daily basis, it’s becoming one of the top five disruptive technologies shaping the language industry.
Wondering if this means that translation, interpreting, language instruction, culture testing and voice over talents as we know today will eventually disappear? We’ve created this guide to show you AI’s implications and we’ll leave it up to you to shape the final outcome.
Here’s how AI is taking the industry to a whole new level:
 1. Neural Text to Speech
1. Neural Text to Speech
On the lines of “Internet of Things”, this AI technology is the “Internet of Voice”. This text to speech (TTS) technology, combined with a wide range of smart technologies allows the user to issue commands and get the response 100% through text. Looking for your next turn in an unfamiliar area? There’s Siri for that. Trying a new recipe and need the directions read to you while you follow the instructions? There’s Google Assistant for that. There are applications in a wide range of scenarios and have been changing the way we interact with our machines, turning our computing experience into a more human experience.
But it’s all about personalization nowadays, isn’t it? The thin line between a human experience and a personal experience is the AI powered TTS technology called neural text to speech.
So, what makes the typical text to speech, neural? It’s built with a neural network which is a type of computer network modeled on the human brain… (continues with same style)
2. Real Time Voice cloning
Voice cloning dates back to 1779 in Russia, when a professor built resonators that mimicked the human voice… (full text here)
- Create indistinguishable speech from the original for game developers or film makers…
- Provide interactive content for E-learning courses…
- Facilitate actors’ work as brand voices…
- Foster the development of a working alliance with clients…
- Set the ideal tone for productions of advertisements…
- Speeds up and eases the dubbing process…
3. Neural Machine Translation
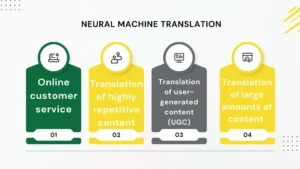
Instead of translating each word individually, it provides automated translation by taking into account the context…
- Online customer service: very useful for staff members…
- Translation of highly repetitive content: such as manuals…
- Translation of user-generated content (UGC) for social sentiment analysis…
- Translation of large amounts of content in the shortest timeframes…
4. AI Dubbing
Back during the good old days, classical dubbing led to a less pleasant experience for the viewer… (full text here)
The Digital Future
So, is AI replacing the language industry? In fact, according to Verified Market Research, the language service industry is projected to reach USD 46.21 Billion by 2027…
- Gain a competitive edge: AI infused translation services keeps the businesses ahead…
- Maximize customer satisfaction: 70%+ of the online users prefer shopping from…
- Widen your business market: AI is allowing businesses to effectively expand…
The fact that there are now websites available to translate for free might have tempted companies and individuals to try, but the results received really drove down the standards…
Saudisoft is constantly working with AI’s emerging technologies, get in touch with Saudisoft’s team to know more.

 1. Neural Text to Speech
1. Neural Text to Speech